Briefing vCenter Server VAMI Interface
Appliance Interface
Appliance management interface is the way you interact with Appliance directly using GUI. So, the same is true for vCenter Server VAMI. you can obtain this Interface by specifying vCenter Server FQDN with port number "5480" using the address bar of the web browser as you can see below
Specify the same user name as you provide for authentication during logon of vCSA.
Summary Page
The very first "Landing" page come up with user logon is the "Summary" that shows basic health of the appliance either good or bad with some other necessary information like Version and build number, Domain joining info, SSO status and Service Health info as you can see below
On the top its a black ribbon as vsphere client got with some options available under "Action" Menu as you can see below
Network Page
Now, lets talk about Network tab, here you can modify configured network adapter card settings for the appliance as you did during deployment phase by providing IP / Subnet Mask , DNS and Gateway settings as you can see below
Monitor & Services Pages
Moreover, you can also setup proxy for vCenter server if required for VCSA to go online through proxy or to access download through FTP server not directly from the internet.
Incase, if you need to look into Health and montior resource utilization than you need to look into three important tabs/pages
- Summary Page
- Monitor Page
- Services Page
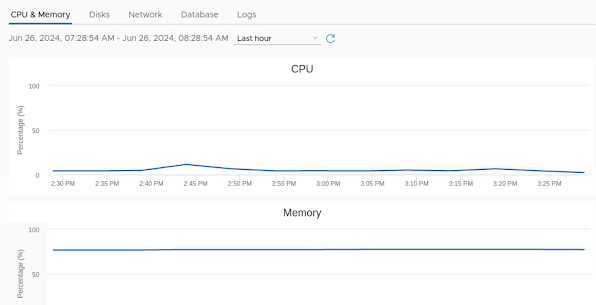
Summary page already explained but in "Monitor" page you can see CPU/Mem utilization and also can see storage performance for this Appliance including Network bandwidth and database performance as well. Below is the snapshot of monitor page that you can easily observe.
Whereas in the "Services" page you can see whether the health of the service is ok and if it is set to automatic than is it running or not. If its not than you can restart the services or set its atart-up type to start with ESXi host as well.
Update Page
Briefing more, you can also setup (Schedule) or update vcenter server appliance through "Update" option as well if you have set-up NATED or proxied settings for updates. Moreover, you can also view the update history as well. But recommendation is to go through Life Cycle Manager to update the stuff.
Time Synch and Settings
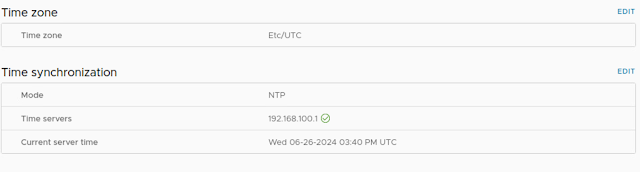
You can also setup NTP server for synchronizing clocks for proper log management using "Time" options. For time source you can use Active Directory Domain Controller (PDC) or Router or Linux appliance etc. Just click "Edit" to modify the IP or settings (Time Zone etc).
Access Page
In-order to provide or enable more than just GUI interface access to vCSA, you can use "Access" page to enable or disable other interfaces like "SSH" or "Power CLI/DCUI" and can also set Bash shell timeout in minutes as well.
Syslog Forward Setting Page
You can set-up central log management as Syslog Collector and point vCenter Serve to that Syslog collector through below settings by specifying IP/FQDN of Syslog Collector server with Port number. By below given settings you can configure syslog setting for this vCSA to forward logs to Syslog collector server.
You can maximum configure upto 3 Syslog collector servers using VAMI Interface of vCenter Server Appliance.
Backup Page
You can do backup of vCSA Configurations and Logs which are sometimes collectively known as SEAT logs (Statistics, Evens, Alarms and Task Logs). This backup takes the backup of configurations in File backup structure instead of image based backup structure which is quite big in size whenever you want to restore where as File based backup can be restore even at granular level which means a single file can be restored instead of the whole image.
- You can take backup of only configuration of vCSA or can couple logs with the configuration as well.
- You can also schedule the backup on Daily, Weekly, Monthly basis or you can immidiately initiate the backup at any time.